Arteriosclerosis definiiton
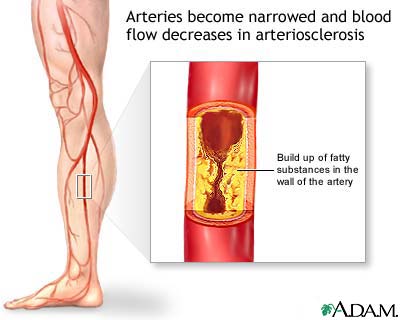
Arteriosclerosis is a degenerative condition of the arteries in which the walls of the arteries become stiff and rigid. Arteriosclerosis is a leading factor in age-related HYPERTENSION (high BLOOD PRESSURE).
There are three forms of arteriosclerosis:
- ATHEROSCLEROSIS in which arterial plaque deposits infiltrate the inner layer of the arterial wall
- Mönckeberg’s arteriosclerosis or medial calcific sclerosis, in which the medial layer of the arterial wall accumulates calcium deposits that cause the ARTERY to become rigid
- arteriolosclerosis in which the arterioles (the threadlike arteries that form the arterial portion of the CAPILLARY BEDS) lose their FLEXIBILITY and elasticity
The primary causes of arteriosclerosis include cigarette smoking (NICOTINE is highly toxic to the smooth MUSCLE fibers of the arteries), DIABETES, and hypertension. The consequences of arteriosclerosis, particularly atherosclerotic, include increased risk for HEART ATTACK, STROKE, ANEURYSM, and increased hypertension. People often use the terms atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis interchangeably, which is not quite accurate though is correct about 90 percent of the time because atherosclerosis is the most common form of arteriosclerosis.
See also DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE; HYPERLIPIDEMIA; LIFESTYLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR HEALTH.