Glucosamine sulfate
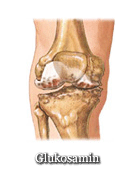
Glucosamine fights against joint injuries. It helps to create cartilage which covers ends of bones and create glenoid epithelium; therefore it helps protect joints and reduces their pain and acampsia. Even though human body is able to produce its own glucosamine, dietary supplements containing glucosamine might be very effective.
Glucosamine is very simple molecule containing glucose. Glucosamine is contained in high concentration in joints and fibrous connective tissue where is used by organism to create all large molecules needed for repairing and protection of cartilage. Over the last years, glucosamine has become a common dietary supplement sold in variety of form – glucosamine sulfate and N-acetylglucosamine (NAG). The best form is glucosamine sulfate in the therapy of arthritis. This form is quickly absorbed in organism (intestines absorb 90 to 98 %) and reduces pains effectively.
Most frequent utilization of glucosamine
Glucosamine kills pain, muscle-bounds, knee and finger edemas, and other joint edemas afflicted with osteoarthritis or rheumatic arthritis. It helps to decrease spondylosis symptoms in neck, chest and loin spine. Glucosamine might fasten the healing of flux, strengthens joints and affects them preventatively from injuries.
Glucosamine sulfate – treatment and effects
Glucosamine can not entirely cure joint disorders. However, it can provide a huge relief for patients suffering of arthritis caused also by ageing (osteoarthritis). Glucosamine might help with therapy of inflammatory diseases such as arthritis.
Glucosamine and its effects:
Glucosamine is used as a cure of joint diseases in 70 world countries; reduces pain and inflammation, and cures ageing and damaged joints. Some research had shown, glucosamine is often more effective than other anti-steroid inflammatory medicaments such as aspirin or ibuprofen usually prescribed to patients. In addition, glucosamine does not have any side effects as those medicaments. Usually prescribed medicine kills pain. Unfortunately, they do not affect organism ability to produce and heal damaged cartilage. In comparison, glucosamine helps to create cartilage and thus heals joint lesions. Unfortunately, glucosamine is not effective in therapy of progressed illness when the cartilage is strongly damaged.
As a substance strengthening joints, glucosamine is beneficial in prevention from arthritis and other degenerative diseases caused by ageing. It might also fasten healing process of injuries, for example sprained ankle or knuckle fluxion.
Recommended dosage of glucosamine
Usual dosage in therapy of arthritis and others diseases is 500 mg of glucosamine sulfate three times a day. This amount is harmless and generally effective.
How to use glucosamine sulfate
Glucosamine is a long term medicine and supposed to be absolutely harmless. Relief is proceeds as quickly as after usage of any other pain killer medicine, usually after two to eight weeks. But it can be faster, and its effects are stronger.
Glucosamine should be used during meals to avoid indigestion. Glucosamine supplements contain a substance similar to cartilage called chondroitin sulfate, and sometimes even substances as niacin or S-adenosylmetionin (SAM). These substances supposedly increase ability to produce new cartilage. Boswelia is an extract from devils claw tree from Namibia, and belongs to supplements similar to glucosamine. Celery seeds and cayenne cream are also known for healing joint illnesses.
Possible side effects of glucosamine
Glucosamine supplements – naturally produced in human body – are truly without contraindication. Digestion difficulties or sickness appears rarely. Glucosamine is recommended to use during meals.
New findings about glucosamine
A daily dosage of 1500 mg of glucosamine sulfate had decreased symptoms of arthritis to 178 patients effectively as 1200 mg of ibuprofen. Furthermore, patients stood the therapy with no difficulties.
Specialists in San Diego suppose, taking glucosamine few days before a surgery might eliminate after surgery cicatrices and reduce complication arising from surgery.
Warnings before usage of glucosamine sulfate
If you have any medical problems, consult using glucosamine with your physician first.
Additional information about glucosamine
Dietary supplements are the most suitable sources of glucosamine. Nutrients containing glucosamine might be crabs, oysters and shrimp shells.
Resource: publication - Leciva moc vitaminu, bylin a mineralnich latek (The salutary power of vitamins, herbs and minerals) Reader´s Digest Choice
Open discussion on the topic Glucosamine sulfate - benefits and side effects
Similar interests
- Nuovi Casino
- Casinos Not On Gamstop
- UK Casinos Not On Gamstop
- Casinos Not On Gamstop
- UK Casinos Not On Gamstop
- Casino Non Aams Italia
- Slot Sites Not On Gamstop
- Meilleur Casino En Ligne
- Non Gamstop Casino Sites UK
- Meilleur Casino En Ligne
- Casino En Ligne France
- Best Non Gamstop Casinos
- Casinos Not On Gamstop
- UK Casino Not On Gamstop
- Casinos Not Signed Up To Gamstop
- Best Slot Sites UK
- Non Gamstop Casino Sites UK
- Online Casinos Nederland
- Online Casinos Nederland
- Casinos Not On Gamstop
- Best New Uk Casinos Not On Gamstop
- Casino Non Aams
- Non Gamstop Casinos UK
- Migliori Siti Casino Non Aams
- Bitcoin Casinos
- Sites De Paris Sportifs Belgique
- Bookmaker Non Aams