Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE)
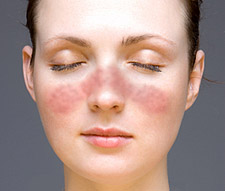
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) is a chronic autoimmune disorder, also called cutaneous lupus erythematosus, in which roughly circular, reddened patches (erythematous lesions) form on the SKIN. The lesions are most common on the face, back of the neck, scalp, inner lips and mouth, and outer portions of the auditory (EAR) canals. The INFLAMMATION involves the epidermis, dermis, and HAIR follicles. When the lesions heal they leave permanent scarring, lightened pigmentation, and loss of hair (ALOPECIA) in their wake. Outbreaks may range from localized and sporadic to generalized and persistent. Cigarette smoking, heat, and exposure to sunlight precipitate or exacerbate outbreaks in many people who have DLE. About 5 percent of people who have DLE subsequently develop SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE), a generalized autoimmune disorder in which lesions can attack internal structures as well as the skin.
Symptoms of Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) and Diagnostic Path
The characteristic appearance of the skin lesions is a clear diagnostic marker for DLE. Because the same skin lesions can be an early indication of SLE, the diagnostic path includes biopsy of representative lesions as well as BLOOD tests to assess ANTIBODY status. People whose DLE lesions are primarily above the neck usually have isolated DLE. People who have DLE lesions both above and below the neck have increased risk for SLE.
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) Treatment Options and Outlook
The primary treatment approach for DLE is topical or injected CORTICOSTEROID MEDICATIONS. In the early stages of the condition, topical corticosteroids often limit the lesion’s progression. As the condition becomes established, the lesions may not respond as well and the dermatologist may inject a corticosteroid medication directly into the lesion. Some people experience relief with medications otherwise prescribed to treat MALARIA, RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS, and severe ACNE, as well as medications that act on the IMMUNE SYSTEM such as the corticosteroids and immunomodulators. These medications have potentially serious side effects and interact with numerous other medications. Women who are pregnant or who could become pregnant cannot take many of them, as they cause damage to the developing fetus.
The use of some of these medications is OFF LABEL USE-that is, not a use the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved though the DRUG itself has FDA approval for other uses. It is important for people who have DLE to discuss with their doctors, and to fully under-stand, the potential benefits and risks of all treatment options. Treatment approaches for DLE target symptoms though do not cure the condition itself.
| MEDICATIONS TO TREAT DLE | |
|---|---|
| Anti-Acne (Retinoids) | |
| isotretinoin | acitretin |
| etretinate | tazarotene |
| Antimalarials | |
| hydroxychloroquine | chloroquine |
| Corticosteroids | |
| triamcinolone | hydrocortisone |
| betamethasone | diflorasone |
| flumethasone | mometasone |
| desoximetasone | halcinonide |
| fluocinonide | amcinonide |
| Immunomodulators | |
| Interferon | thalidomide |
| azathioprine | mycophenolate |
| methotrexate | dapsone |
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) Risk Factors and Preventive Measures
Researchers do not know for certain what autoimmune mechanisms cause the lupus disorders, or what triggers them. Because DLE and SLE seem to run in families, a genetic component is likely. At present there are no known preventive measures. Though women are more likely than men to develop DLE, there are no clear risk factors for the condition other than family history. Early treatment minimizes the residual scarring, atrophy, alopecia (hair loss), and other permanent consequences the lesions can cause.
Cigarette smoking worsens the lesions, so doctors strongly advise people who have DLE and smoke to stop. Sun exposure also increases the frequency and number of lesions; liberal application of high-SPF sunscreen and sun-blocking clothing can mitigate this effect.
See also AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS; LEUKOPLAKIA; LESION; LICHEN PLANUS; SARCOIDOSIS; SJÖGREN’S SYNDROME; SMOKING CESSATION; SUN PROTECTION.