Cytomegalovirus / CMV virus - Symptoms, causes and treatment
What is Cytomegalovirus - CMV virus and causes
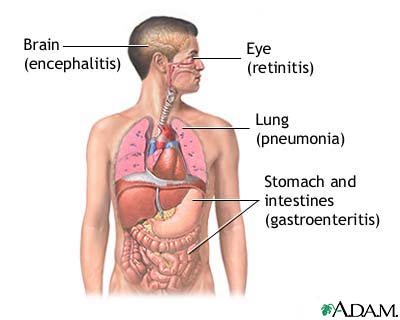
Cytomegalovirus / CMV virus - a member of the herpesvirus family, also called human herpesvirus-5 (HHV-5). Like other herpesviruses, CMV is ubiquitous throughout the world-85 percent of Americans have CMV INFECTION by age 40. However, CMV infection primarily causes illness only in people who are IMMUNOCOMPROMISED, such as people who have HIV/AIDS or who take long-term IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE THERAPY after ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION. CMV is also a significant risk for the unborn child of a woman whose initial infection with the VIRUS occurs during PREGNANCY. CMV virus crosses the PLACENTA to the fetus, causing congenital CMV infection. Most infants are born unharmed; however, CMV infection can affect hearing, vision, and intellectual capacity.
Symptoms of Cytomegalovirus / CMV virus and Treatment
When CMV infection causes illness, symptoms typically include NAUSEA, VOMITING, DIARRHEA, JAUNDICE, and FEVER. The person often has an enlarged and tender LIVER (HEPATOMEGALY) and SPLEEN (SPLENOMEGALY). Doctors may suspect infectious mononucleosis or HEPATITIS, though tests for these conditions come back negative. A BLOOD test can detect the presence of CMV antibodies to confirm the diagnosis of CMV infection. Though most people recover without complications, CMV infection can be serious or fatal in people who are immunocompromised. ANTIVIRAL MEDICATIONS are not very effective in treating the infection; treatment primarily targets symptoms.
See also ANTIBODY; EPSTEIN-BARR VIRUS; HERPES SIMPLEX; HERPES ZOSTER; MONONUCLEOSIS, INFECTIOUS; OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTION.