Pneumococcal pneumonia - symptoms and treatment
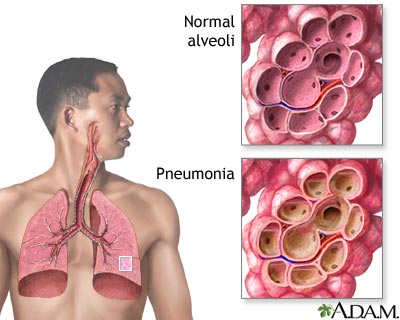
What is Pneumococcal pneumonia
Pneumococcal pneumonia - An illness resulting from INFECTION with the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is normally present in the mucous membranes of the NOSE and sinuses. Researchers do not know what processes occur in the body that allow S. pneumoniae to shift from NORMAL FLORA to causing infection in its native environment. Pneumococcal pneumonia is a serious upper respiratory illness that can invade the LUNGS and spread to the BRAIN (causing MENINGITIS) and middle EAR (causing OTITIS media). Pneumococcal pneumonia can also cause SEPTICEMIA, a lifethreatening illness of widespread bacterial infection that involves multiple organ systems.
Symptoms of Pneumococcal pneumonia and Diagnostic Path
Symptoms begin suddenly and are usually severe. They include
- a shaking chill followed immediately by sudden high FEVER
- nonproductive COUGH
- difficulty BREATHING (DYSPNEA) and CHEST PAIN
- HEADACHE
- NAUSEA and VOMITING
- fatigue
The diagnostic path includes chest X-RAY and BLOOD or fluid tests to determine the presence of S. pneumoniae. Because symptoms are severe and the risk for complications is high, doctors typically begin immediate treatment with ANTIBIOTIC MEDICATIONS. Symptoms that dramatically improve with the first 24 hours of treatment further confirm the diagnosis.
Pneumococcal pneumonia Treatment Options and Outlook
Penicillin is the antibiotic of first choice for treatment, though about 25 percent of S. pneumococcal strains are now resistant to it. Most resistant strains are sensitive to other antibiotic medications. The antibiotic of last resort is vancomycin, which doctors reserve for pneumonia that does not respond to treatment with any other antibiotics. With appropriate antibiotic therapy many people fully recover from pneumococcal pneumonia, though it is important to take the full course of antibiotics even after symptoms are gone. Pneumococcal pneumonia can be fatal.
| ANTIBIOTIC MEDICATIONS TO TREAT PNEUMOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA | |
|---|---|
| cefotaxime | ceftizoxime |
| ceftriaxone | clindamycin |
| erythromycin | gatifloxacin |
| grepafloxacin | levofloxacin |
| penicillin | moxifloxacin |
| sparfloxacin | vancomycin |
Risk Factors and Preventive Measures
People most vulnerable to pneumococcal pneumonia are the very young, the very old, and those who are IMMUNOCOMPROMISED. The pneumococcal VACCINE, administered each year, can prevent S. pneumoniae infection.
See also ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE; INFLUENZA; INFLUENZA PREVENTION.