Splenectomy - Removal of spleen
Splenectomy is a surgical OPERATION to remove the SPLEEN. Though the spleen performs many vital immune and BLOOD-related functions, it is not essential for life. Because the spleen contains 4 percent of the body’s blood volume and a third of its platelets, it is vulnerable to life-threatening hemorrhage with trauma. Doctors may also choose to remove the spleen for therapeutic or prophylactic (preventive) reasons in conditions such as chronic myeloid LEUKEMIA and MYELOFIBROSIS.
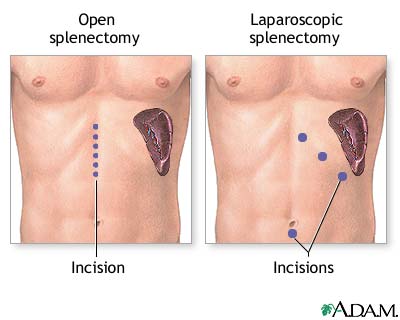
Splenectomy may be an OPEN SURGERY or a laparoscopic surgery, depending on the reason and the person’s overall health status, performed under general ANESTHESIA. Laparoscopic splenectomy, which involves removing the spleen using a lighted endoscope and small tools the surgeon inserts through four or five small incisions in the upper left abdomen, usually requires an overnight stay in the hospital with three to four weeks for full recuperation. Open splenectomy requires a single incision, four to five inches long, through which the surgeon opens the abdominal cavity and removes the spleen. The open surgery may require three to five days in the hospital with four to six weeks for full recovery.
| COMMON REASONS FOR SPLENECTOMY | |
|---|---|
| hemolytic ANEMIA | LEUKEMIA |
| LYMPHOMA | PORTAL HYPERTENSION |
| THROMBOCYTOPENIA | trauma with hemorrhage |
| uncontrolled SPLENOMEGALY | |
As with any surgery, excessive bleeding and INFECTION are potential risks. Because absence of the spleen compromises the body’s IMMUNE RESPONSE, lowered resistance to infection is a common consequence of splenectomy. Doctors recommend pneumococcal PNEUMONIA vaccination before splenectomy when possible and immediately after when splenectomy is an emergency surgery. The doctor may recommend other immunizations, depending on individual health circumstances. People who have had splenectomy must remain diligent in regard to potential infections, even those that are seemingly minor such as COLDS. Many doctors recommend ANTIBIOTIC PROPHYLAXIS (preventive ANTIBIOTIC MEDICATIONS) to offset the IMMUNE SYSTEM’s diminished response.
See also SURGERY BENEFIT AND RISK ASSESSMENT.