Allergic asthma treatment and symptoms
What is Allergic Asthma and definition
Allergic asthma is a HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTION (allergic reaction) that involves the airways (bronchi). allergic ASTHMA is a type I or IMMUNOGLOBULIN E (IgE) reaction. Mast cells in the bronchial membranes release HISTAMINE, PROSTAGLANDINS, and LEUKOTRIENES. These substances cause itching and swelling of the bronchial membranes, resulting in wheezing and the sensation of chest tightness.
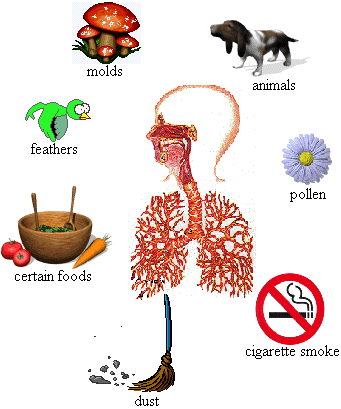
Cockroach droppings are the most frequent cause of allergic asthma. Other common allergens for allergic asthma include pollens (trees, grasses, and weeds), dust and dust mites, cigarette smoke, molds, and pet dander (especially cat dander). About 70 percent of people who have allergic asthma also have ALLERGIC RHINITIS, also called seasonal allergies or hay FEVER.
Symptoms of Allergic Asthma
The diagnostic path focuses on separating allergic from nonallergic asthma. Though the symptoms are the same, the mechanisms and treatment approaches are different. Symptoms of allergic asthma include wheezing, shortness of breath (DYSPNEA), sensation of being unable to get enough air, and coughing. A severe hypersensitivity reaction, ANAPHYLAXIS, may occur if the bronchi swell enough to prevent the flow of air into the LUNGS.
ANAPHYLAXIS is a potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate care from a doctor or hospital emergency department.
Allergic Asthma Treatment
Treatment for allergic asthma may include oral and inhaled ANTIHISTAMINE MEDICATIONS, corticosteroid medications, and leukotriene receptor antagonist medications. Omalizumab (Xolair), a monoclonal antibody administered via subcutaneous injection, dramatically drops IgE levels in the BLOOD circulation, effectively stopping the hypersensitivity reaction before it causes symptoms. The most effective treatment is avoiding known or suspected allergens, though this is not always possible. ALLERGY TESTING can determine the specific allergens responsible for symptoms. DESENSITIZATION, in which the allergist exposes the person to small but increasing doses of the allergen over time, can help reduce the immune response to the allergen.
See also ALLERGIC CONJUNCTIVITIS; ALLERGIC DERMATITIS; ALLERGY; ANTIGEN; ATOPY; BREATH SOUNDS; CYTOKINES; LIVING WITH ALLERGIES; MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES (MABS).