Carpal Tunnel Syndrome - treatment, symptoms, exercises and surgery
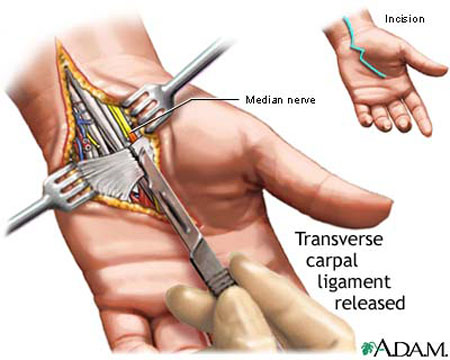
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a collection of symptoms resulting from compression of the median NERVE as it passes through the carpal tunnel, a narrow channel in the carpal bones of the wrist. The ligaments that form the carpal tunnel can become irritated and inflamed, constricting the median nerve and the tendons in the area. The median nerve supplies the inside of the hand, the thumb, and the first three fingers (the ulnar nerve supplies the outside of the hand and the little finger). Compression of the nerve affects sensation and function in the hand.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Diagnostic Path
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome progress gradually over months to years. They may include
- tingling
- numbness
- weakness
- loss of ability to use the thumb and first two or three fingers
- PAIN that shoots from the hand up the forearm
Some people also experience perceptible swelling and tenderness to touch over the wrist. Symptoms are generally intermittent at the onset and progress to occur more frequently and have greater intensity. The diagnostic path includes tests of the hand and wrist that are able to bring on or intensify the symptoms. The doctor may order electromyogram (EMG) and nerve conduction studies for further diagnostic information.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment Options and Outlook
Treatment efforts attempt to manage symptoms conservatively, with measures such as NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDS), injection of a corticosteroid, and splinting. When fluid retention (edema) is a factor, diuretic medications (“water pills”) may help. Some people experience improvement in their symptoms when they take vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) supplements. Certain YOGA postures that increase FLEXIBILITY and STRENGTH of the wrists improves symptoms for some people. Surgery, either open or laparoscopic, to cut the carpal LIGAMENT is the curative treatment for most people who have carpal tunnel syndrome. Such an OPERATION opens the carpal tunnel, relieving compression against the median nerve. Full recovery from the open procedure takes about 12 weeks and from the laparoscopic procedure about 8 weeks. A rare complication of carpal tunnel surgery is permanent weakness in the hand as a consequence of cutting the median nerve. Other possible complications, also rare, include excessive bleeding and postoperative INFECTION.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Risk Factors and Preventive Measures
Doctors believe many people who develop carpal tunnel syndrome have an inherently narrow carpal tunnel, making the passage tighter. Women, who have smaller BONE structures than men, are three times more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome. Carpal tunnel syndrome may also follow injury to the wrist, such as strain or FRACTURE, or accompany OSTEOARTHRITIS of the wrist. People who have DIABETES, PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE (PVD), and other conditions associated with NEUROPATHY (injury to the nerves) are particularly susceptible to compression syndromes such as carpal tunnel syndrome.
Work that subjects the wrists to continuous vibration or repetitive movement also increases the risk for carpal tunnel syndrome. The highest risk is among people who do assembly-line work, such as in manufacturing, professional sewing, meat packing, and poultry processing. Job tasks in these occupations subject the wrists to repeated flexing under pressure. Though occupations involving extensive typing, keyboarding, or data entry were long suspected as prime causes of carpal tunnel syndrome, recent studies support only a slight increase in risk. Frequent short breaks to stretch and flex the wrists during work and wearing supportive wrist braces can help prevent carpal tunnel syndrome or minimize its symptoms.
See also ENDOSCOPY; OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY; REPETITIVE MOTION INJURIES; SPRAINS AND STRAINS; SURGERY BENEFIT AND RISK ASSESSMENT; TENDON.